Salicylate sensitivity is best known for its association with aspirin sensitivity with the most common symptoms involving the skin, digestive or respiratory systems. Others symptoms involving the nervous system (autonomic, central) have been observed in a small percentage of people.
| · Rashes, hives, tingling /rash on lips | · Anxiety, panic attacks |
| · Symptoms of ADHD / ADD | · Sleep disturbances |
| · Asthma | · Nausea |
| · Eczema | · Flatulence |
| · Sinusitis | · Irritability, restlessness |
| · Rhinitis | · Rapid heart beat |
| · Headaches and migraines | · Tinnitus |
| · Stomach aches | · Constant clearing of throat |
| · Bloating | · Joint pain |
To diagnose an intolerance to salicylates, a healthcare professional will usually take a detailed history of diet and related symptoms. People who are very sensitive to dietary salicylates may require a salicylate-restricted diet under the direction of a doctor or registered dietitian.
As sensitivity to one food chemical increases the risk of sensitivity to others, investigated may be intolerance to other food chemicals as well. This is done by doing the RPAH Allergy Unit Elimination Diet.
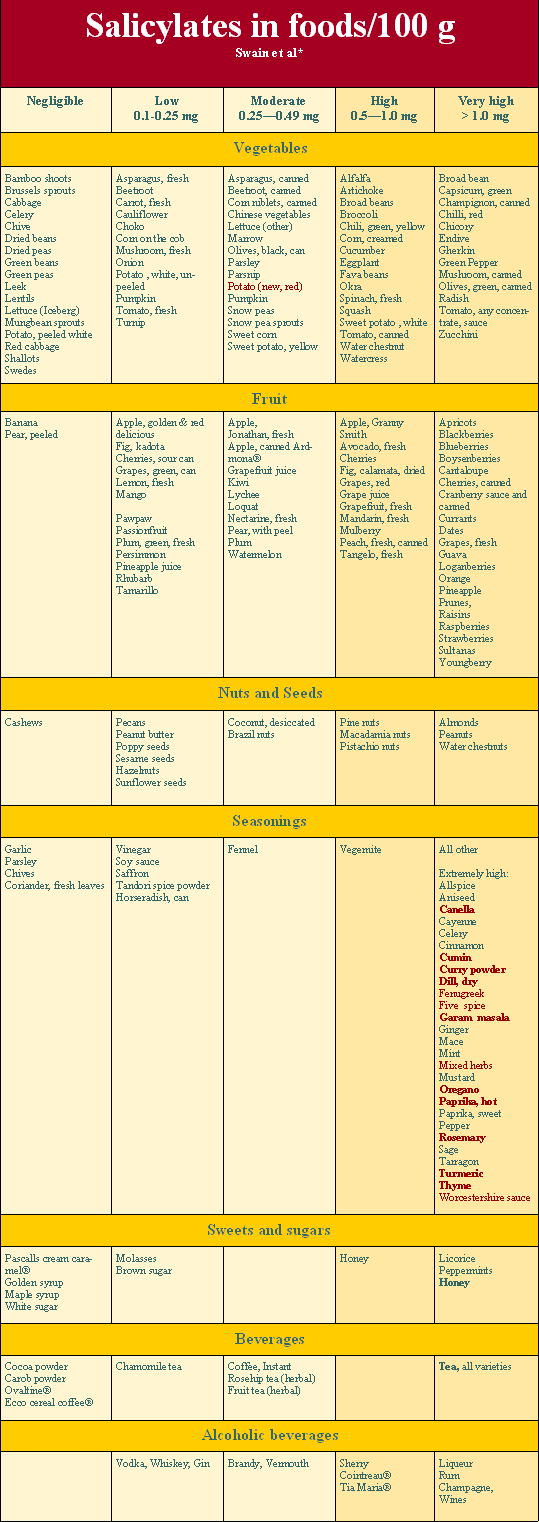
During the elimination diet people are generally advised to eat only low foods for 3 to 4 weeks to see if symptoms improve. If symptoms do improve it confirms intolerance, at which stage the persons diet is usually liberated by introducing some moderate foods and so on.
Unless symptoms are severe some people prefer to do a simpler approach of just restricting very high foods.
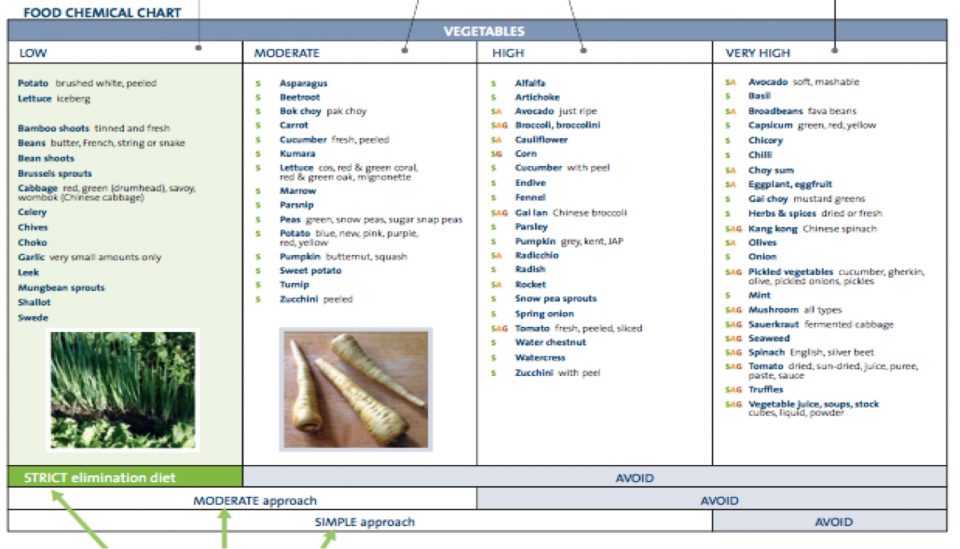
Low salicylate foods include all fresh meat, poultry, eggs, dairy, shellfish and grains and cereals.
Other Sources of Salicylates can be a concern for people with confirmed salicylate
Fortunately there are low salicylate (fragrance free) choices available.
| Acne products Air fresheners Alka seltze Breath mints Bubble baths Cleaning products Cosmetics Detergents | Essential oils Fabric conditioners Fragrances and perfumes Hair sprays, gels and mouse Lotions and creams Lozenges Mouthwash Muscle and joint pain creams | Razor’s with aloe strips next to the blade Shampoo and conditioners Shaving cream Cleansers and exfoliants Soaps Sunscreen and tanning lotion After sun lotions Toothpaste Warts and callus removers |
Salicylates may be labeled as:
| Acetylsalicylic acid Coal tar derived dye Artificial flavorings Artificial colorings Azo dyes Benzyl salicylate Beta hydroxy acid BHA BHT Choline salicylate | Ethyl salicylate Eucalyptus oils Isoamyl salicylate Magnesium salicylate Menthol Methyl salicylate Mint Octylsalicylate Oil of wintergreen Peppermint | Phenylethyl salicylate Red dye (#40) Salicylaldehyde Salicylamide Salicylate Salicylic acid Sodium salicylate Spearmint Yellow dye (#5 and #6) |
What non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) contain salicylates?
| OVER THE COUNTER | PRESCRIPTION | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | Celecoxib | Ketorolac | Naproxen |
| Aspirin | Diclofenac | Ketoprofen | Parecoxib |
| Etoricoxib | Mefenamic Acid | Piroxicam | |
| domethacin | Meloxicam | Sulindac |
What food additives contain salicylates?
| FOOD DYES | FOOD DYES | FOOD PRESERVATIVES | FOOD FLAVOURINGS |
|---|---|---|---|
| E102 Tartrazine | E123 Amaranth | E210-219 Benzoates | E622-623 Glutamates |
| E104 Quinoline yellow | E124 Ponceau 4 R | E220 Sulphur dioxide | |
| E107 Yellow 2G | E132 Indigo carmine | E221-227 Sulphites | |
| E120 Cochineal, Carmine | E127-180 Other food dyes | E250-251 Nitrites, nitrates | |
| E122 Carmoisine | E310-312 Gallates | ||
| E320-321 BHA and BHT |